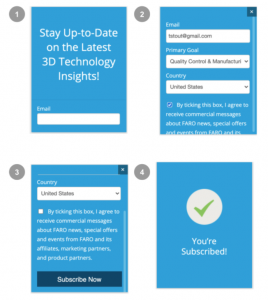
Use Journey Mapping to Increase Web Form Conversion Rates
Design a User-Centric Journey for Conversion!
By David Pfeiffer
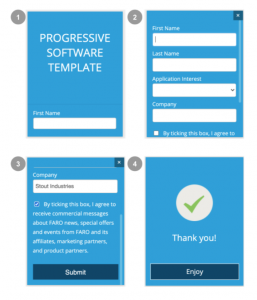
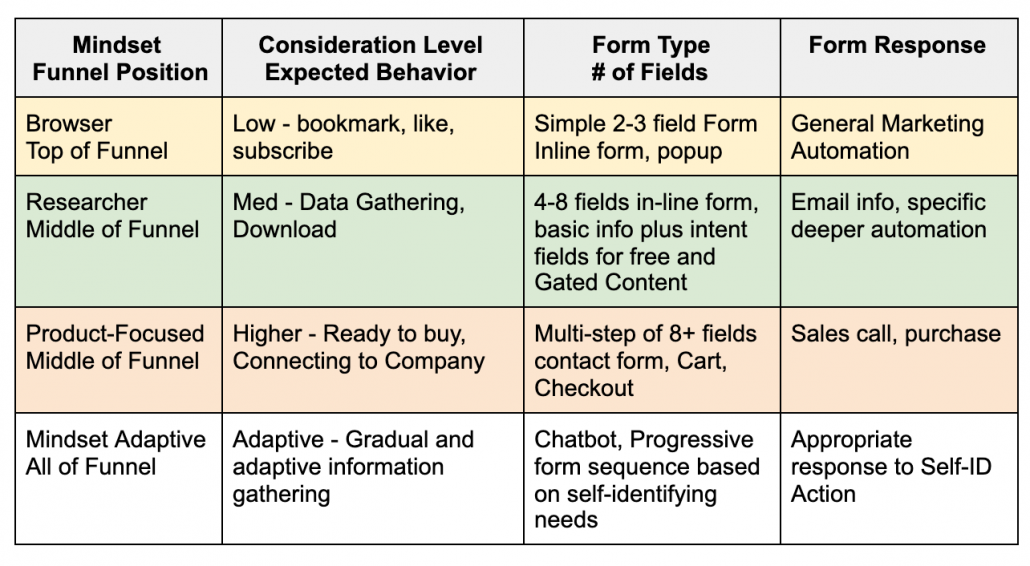
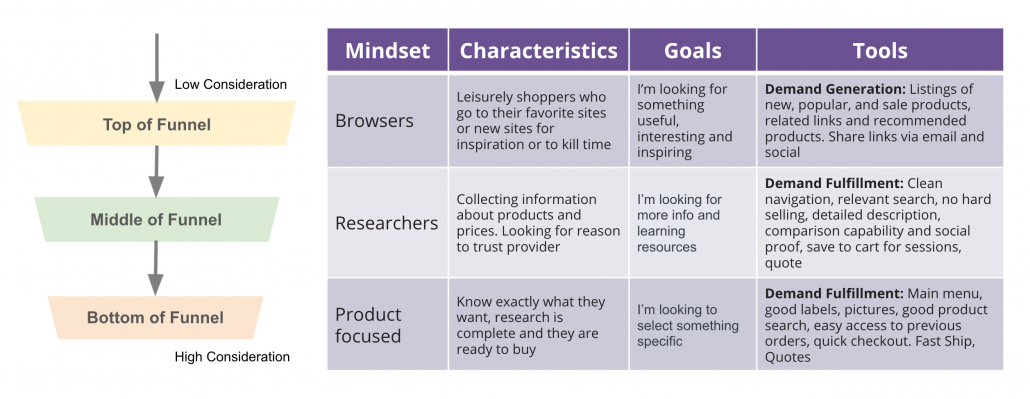
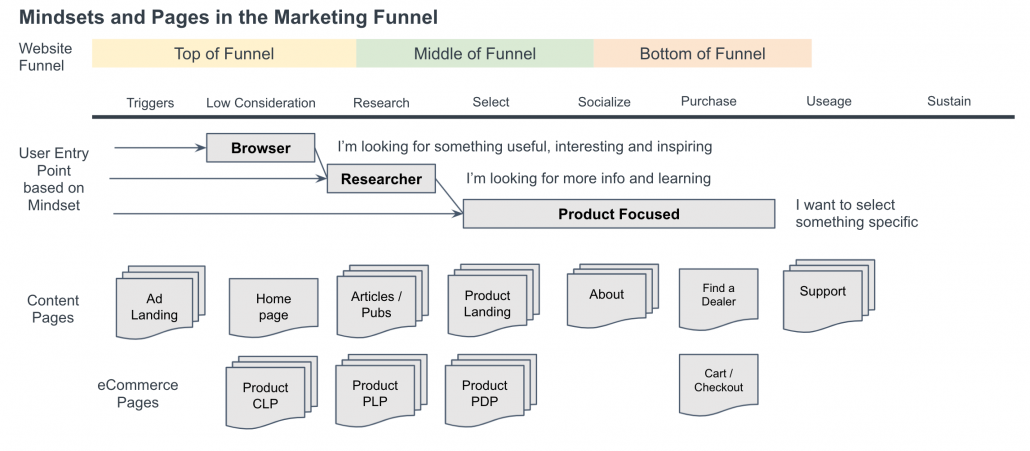
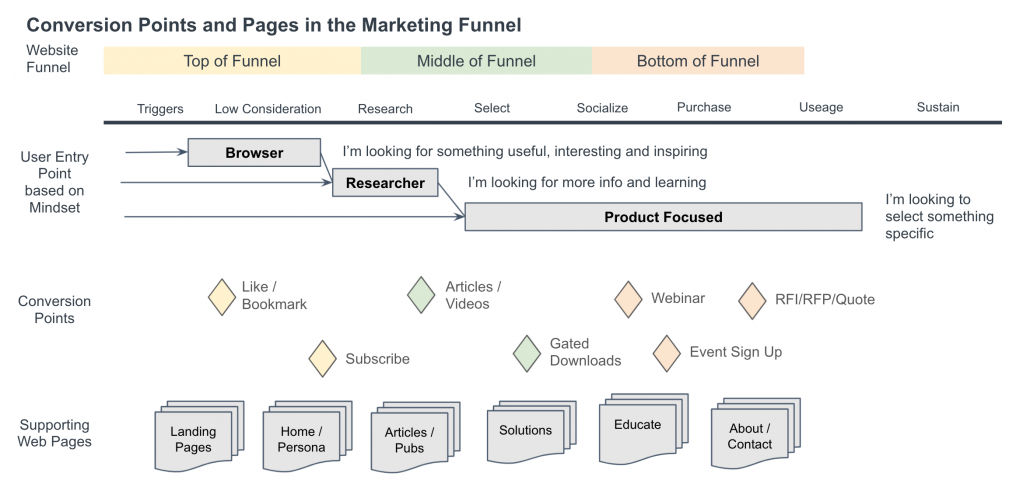
User-Centric Journey for Web Forms
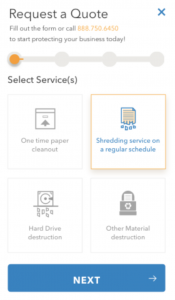
Are your web forms converting above the typical rates?
Assuming your SEO efforts bring relevant traffic to your website, you should expect a healthy form completion rate. If not, read this article on how to present the right form at the right time.
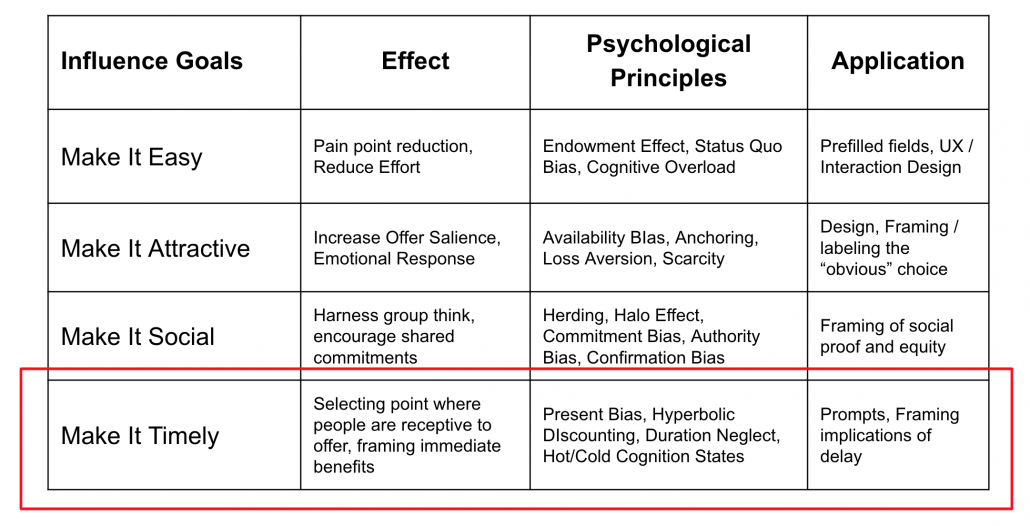
Emotional Decision Making
Although we think of ourselves as highly rational decision-makers, behavioral scientists have repeatedly shown that we take our emotions into account when making decisions. Without some emotional input, we tend to dither over small details and endless comparisons, thereby making no decisions. A no-pain, emotive message is important to high form conversion rates.



 .
.